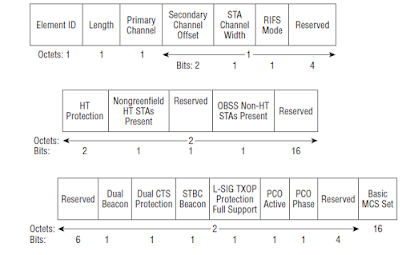
MIMO - 802.11ac
Reference https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0fpyfPUyfic Multipath: A signal from the transmitter may travel through different paths due to reflections from obstacles along the path. These signals arrive at different times and different angles at the receiver and interfere with signal from direct line of sight. This causes distortion of signal at the receiver. Prior to 802.11n this multi-path had a adverse effect. But from 802.11n , the multi path effect has been used constructively, 1. Using spatial multiplexing, different data streams are transmitted from different antennas 2. Transmit diversity, where the same data is sent through different transmitter radio chain and processed at the receiver 3. Multiple identical data streams received at the the receiver by different radio chains can be processed using MRC algorithms Multi path is a requirement for sending multiple streams. If multipath effect is not there , multiple spatial streams cannot be sent. For example in the outdoor